The Smart5Grid project’s main aim is to use 5G to revolutionize the energy sector, introducing the concept of Network Apps and the related new paradigm in virtualization.
This approach enables flexibility, scalability, for energy verticals via efficient resource use and rapid deployment of services.
Network Apps adoption will facilitate the creation of a dynamic marketplace, encouraging innovation among IT sectors, SMEs, and startups.
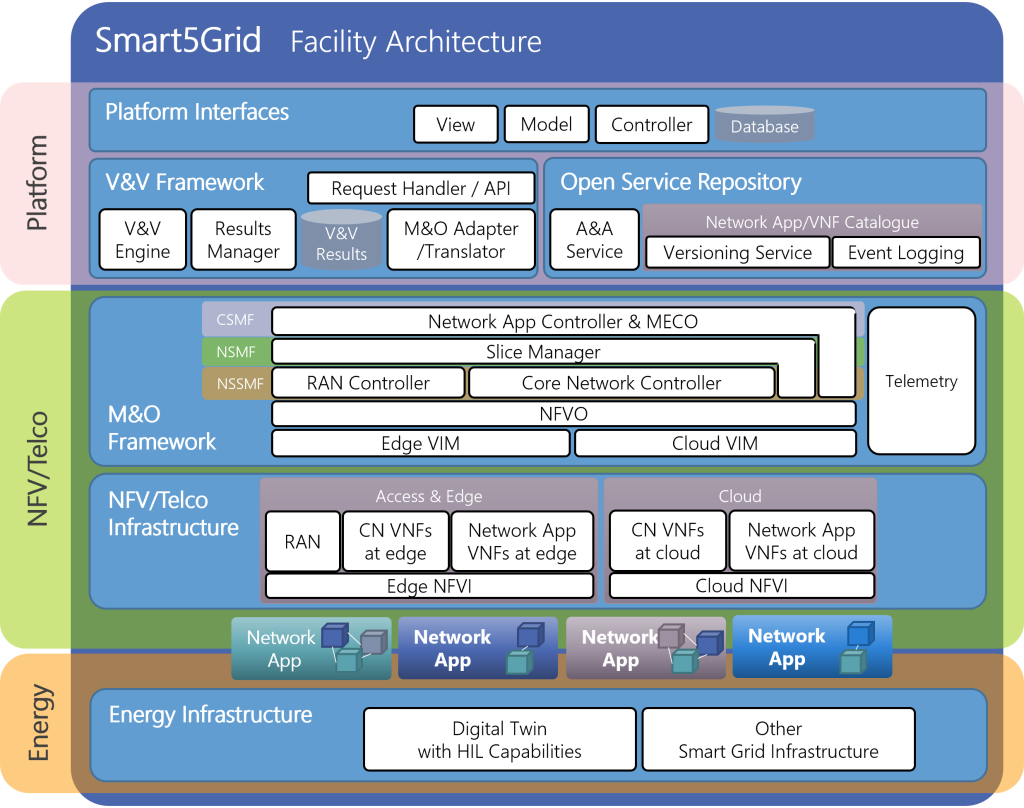
The main enabler for this new paradigm is the Smart5Grid reference Architecture stack that has 3 main layers:
- Layer One: The Platform– At the heart of Smart5Grid sits the platform where you’ll find the Open Service Repository (OSR) that is responsible for the storage and management of Network Apps and VNFs and at the same time constitutes the intuitive platform interface for the end users and the Verification and Validation (V&V) framework.
- Layer Two: The Connectivity NVF / TELCO layer- Where virtualization and the telecommunication meet and operate with state-of-the-art management and orchestration functions.
- Layer Three: Smart Energy Grid Layer: Where the smart grid infrastructure is seamlessly integrated with the Network App services.
List of Acronyms
API -Application Programming Interface
V&V – verification and validation
M&O -management and orchestration
A&A – Authentication & Authorisation
VNF – Virtual Network Function
MECO – Multi-access Edge Computing Orchestrator
RAN – Radio Access Network
NFVO – Network Function Virtualization Orchestrator
VIM – Virtual Infrastructure Manager
CN – Core Network
NFVI – Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure
HIL – Hardware-in-the Loop
Smart5Grid platform layer
The platform layer is the uppermost part of the architecture and is the entry point for 3rd party users to the Smart5Grid facility. This point of entry is provided by the User Interface, a web application that manages the authorization and authentication and provides access to the services offered by the exposed APIs of the OSR.
The OSR is the component responsible for the storage and management of Network Apps and Virtual Network Functions (VNFs). It provides a unified service to the users, offering access to existing Network Apps as well as a complete toolset for the implementation of modern DevOps practices to users developing Network Apps.
Before the Network Apps and VNFs are stored in the OSR, these are tested through another important component of Smart5Grid, the V&V framework.
The V&V aims is to facilitate the deployment of Network Apps in the 5G infrastructure, offering testing and deployment capabilities in this infrastructure. Developers can analyse and validate their solutions to ensure they meet the expected standards and consequently making the deployment process faster since errors and anomalous behaviours can be detected, using S5G testing environment.
The V&V framework is composed of two main engines: Verification and Validation. The verification engine assesses the syntax, integrity, and topology of the Network Apps and/or VNFs while the validation engine provides the onboarding and instantiation in a particular Management and Orchestrator M&O framework.
NFV / Telco layer
This layer contains the required computing and networking systems that enable the deployment of Network Applications for its validation by the V&V framework. It is subdivided in two parts: the Management and Orchestration (M&O) framework, and the NFV/Multiaccess Edge Computing (MEC)/Telco Infrastructure itself.
The M&O framework enables a wide range of functionalities and for network orchestration, including the Slice Manager and Network controllers. The Network App Controller (NAC/MECO) is an integral part of this, specifically tasked to manage the end-to-end lifecycle of a Network App deployment. This includes monitoring and controlling of the various stages such as onboarding, instantiation, monitoring, scaling, and termination.
The required NFV/MEC/Telco infrastructure is of two kinds primarily: computing and networking. The computing infrastructure is utilized by the M&O framework to deploy the software components in the form of containers that constitute a Network App. This computing infrastructure can be centrally located or placed at the edge to benefit from reduced latency communications. The networking infrastructure is formed of networking nodes in both access and core domains such as 5G gNodeBs and 5G Core Network functions, which may be configured to meet the traffic demands of a Network App.
Smart Energy Grid Layer
The Energy Infrastructure layer is composed of diverse devices spanning from generation to consumption segment of the network. This includes not just the main segments of transmission and distribution but also comprises devices essential for the grid’s operation and maintenance, like cameras, sensors, and advanced measurement units such as phasor measurement units.
In this layer data is produced by sensors and consumed by intelligent controllers of distributed energy resources, automated remote terminal units, and applications tailored to guarantee the grid’s reliable function. These devices are the ultimate subject of the function performed by the Network Apps. Through the Telco network, devices can reach the NFV infrastructure where the Network Apps components are executed and connect to their offered services.
Such infrastructure is mandatory especially during the preliminary stages of testing and validating the software tools developed.
For more detailed information, please, check deliverables D2.2, D3.1, D3.2, D4.2